Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Multi-scale Gaussian Normalization#
This example applies Multi-scale Gaussian Normalization
to a SunPy Map using sunkit_image.enhance.mgn.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sunpy.data.sample
import sunpy.map
from astropy import units as u
from matplotlib import colors
import sunkit_image.enhance as enhance
SunPy sample data contains a number of suitable images, which we will use here.
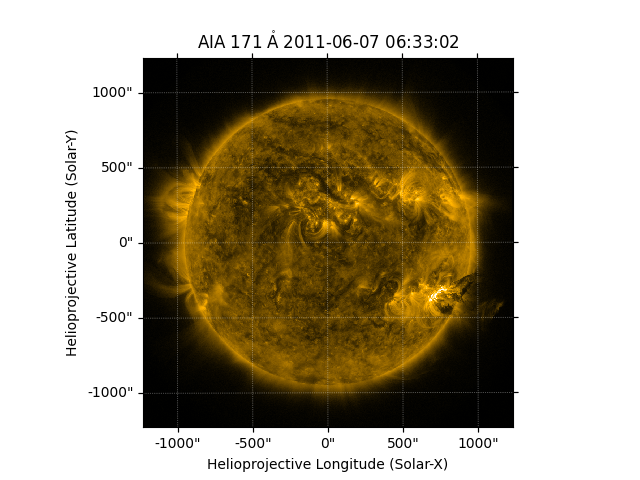
aia_map = sunpy.map.Map(sunpy.data.sample.AIA_171_IMAGE)
# The original image is plotted to showcase the difference.
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.subplot(projection=aia_map)
aia_map.plot(clip_interval=(1, 99.99) * u.percent)
Files Downloaded: 0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?file/s]
AIA20110607_063302_0171_lowres.fits: 0%| | 0.00/973k [00:00<?, ?B/s]
AIA20110607_063302_0171_lowres.fits: 60%|██████ | 585k/973k [00:00<00:00, 5.62MB/s]
Files Downloaded: 100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 4.33file/s]
Files Downloaded: 100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 4.32file/s]
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage object at 0x7f7cb438ea80>
Applying Multi-scale Gaussian Normalization on a solar image.
The sunkit_image.enhance.mgn function takes a numpy.ndarray as a input so we will pass only
the data part of GenericMap
out = enhance.mgn(aia_map.data)
# The value returned is also a numpy.ndarray so we convert it back to
# a sunpy.map.GenericMap.
out = sunpy.map.Map(out, aia_map.meta)
Now we will plot the final result.
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.subplot(projection=out)
out.plot(norm=colors.Normalize())
plt.show()

Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 4.072 seconds)