Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Tracing Coronal Loops#
This example traces out the coronal loops in a FITS image
using occult2. In this example we will use the settings
and the data from Markus Aschwanden’s tutorial on his IDL implementation of
the OCCULT2 algorithm, which can be found
here.
The aim of this example is to demonstrate that occult2 provides similar
results compared to the IDL version.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import sunpy.map
from astropy import units as u
from astropy.io import fits
import sunkit_image.trace as trace
We will be using astropy.io.fits.open to read the FITS file from the tutorial website
and read in the header and data information.
hdu = fits.open("http://data.sunpy.org/sunkit-image/trace_1998-05-19T22:21:43.000_171_1024.fits")[0]
# We can now make this into a `sunpy.map.GenericMap`. There is currently not an instrument specific
# class for the TRACE instrument.
trace_map = sunpy.map.Map(hdu.data, hdu.header)
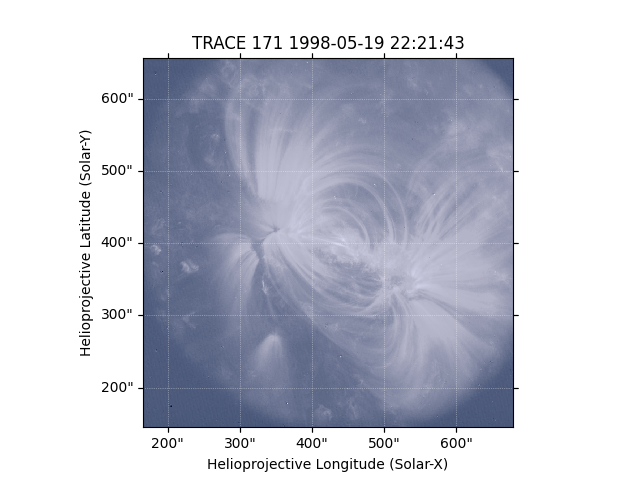
# We can now plot the map, of which we can see coronal loops.
trace_map.plot()
INFO: Missing metadata for solar radius: assuming the standard radius of the photosphere. [sunpy.map.mapbase]
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/sunkit-image/conda/stable/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sunpy/map/mapbase.py:632: SunpyMetadataWarning: Missing metadata for observer: assuming Earth-based observer.
For frame 'heliographic_stonyhurst' the following metadata is missing: hgln_obs,hglt_obs,dsun_obs
For frame 'heliographic_carrington' the following metadata is missing: crlt_obs,crln_obs,dsun_obs
obs_coord = self.observer_coordinate
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage object at 0x7fd550ed3fa0>
Now the loop tracing will begin. We will use the same set of parameters
as in the IDL tutorial.
The lowpass filter boxcar filter size nsm1 is taken to be 3.
The minimum radius of curvature at any point in the loop rmin is 30 pixels.
The length of the smallest loop to be detected lmin is 25 pixels.
The maximum number of structures to be examined nstruc is 1000.
The number of extra points in the loop below noise level to terminate a loop tracing ngap is 0.
The base flux and median flux ratio qthresh1 is 0.0.
The noise threshold in the image with respect to median flux qthresh2 is 3.0 .
For the meaning of these parameters please consult the OCCULT2 article.
loops = trace.occult2(trace_map.data, nsm1=3, rmin=30, lmin=25, nstruc=1000, ngap=0, qthresh1=0.0, qthresh2=3.0)
occult2 returns a list, each element of which is a detected loop.
Each detected loop is stored as a list of x positions in image pixels, and a list of y
positions in image pixels, of the pixels traced out by OCCULT2.
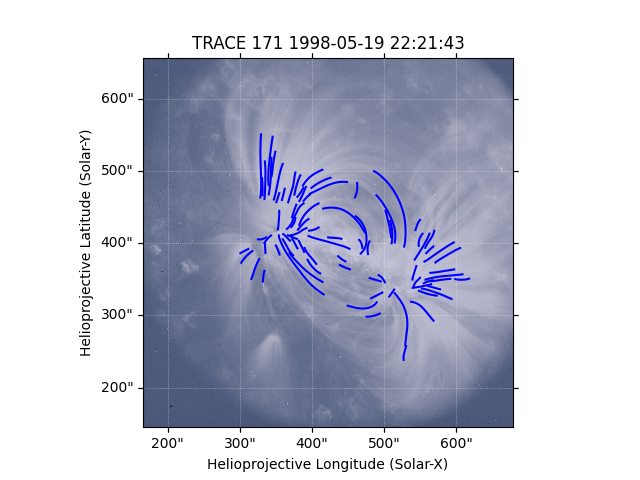
Now plot all the detected loops on the original image, we convert the image pixels to
to world coordinates to be plotted on the map.
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.subplot(projection=trace_map)
trace_map.plot()
# We can now plot each loop in the list of loops. We plot these in world coordinates, converting them
# through the `pixel_to_world` functionality which converts the pixel coordinates to coordinates (in arcsec)
# on the `trace_map`.
for loop in loops:
loop = np.array(loop) # convert to array as easier to index `x` and `y` coordinates
coord_loops = trace_map.pixel_to_world(loop[:, 0] * u.pixel, loop[:, 1] * u.pixel)
ax.plot_coord(coord_loops, color="b")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 31.056 seconds)