Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Drawing and using a Great Arc#
How to define and draw a great arc on an image of the Sun, and to extract intensity values along that arc.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import astropy.units as u
from astropy.coordinates import SkyCoord
from astropy.visualization import quantity_support
import sunpy.map
from sunpy.coordinates.utils import GreatArc
from sunpy.data.sample import AIA_171_IMAGE
quantity_support()
<astropy.visualization.units.quantity_support.<locals>.MplQuantityConverter object at 0x7fe8560e51b0>
We start with the sample data.
m = sunpy.map.Map(AIA_171_IMAGE)
Let’s define the start and end coordinates of the arc.
Create the great arc between the start and end points.
Plot the great arc on the Sun.
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(projection=m)
m.plot(axes=ax, clip_interval=(1, 99.99)*u.percent)
ax.plot_coord(great_arc.coordinates(), color='c')
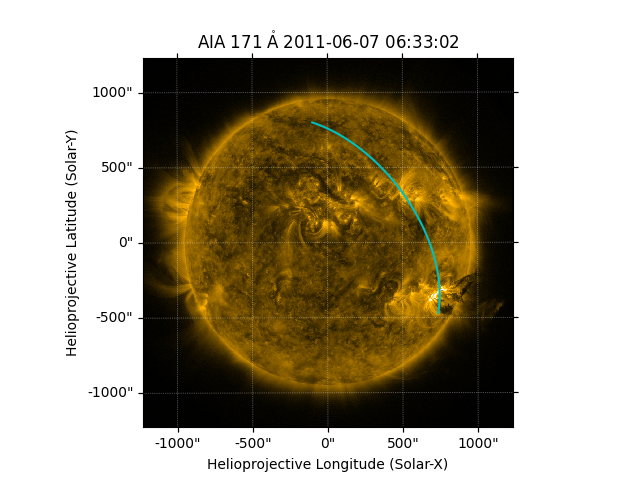
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x7fe854feece0>]
Now we can get the intensity along the great arc coordinates, along with the angular distance from the start of the arc
coords = great_arc.coordinates()
intensity_coords = sunpy.map.pixelate_coord_path(m, coords)
intensity = sunpy.map.sample_at_coords(m, intensity_coords)
separation = intensity_coords.separation(intensity_coords[0]).to(u.arcsec)
Plot the intensity along the arc from the start to the end point.
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(separation, intensity)
ax.set_xlabel(f'Separation from start of arc [{separation.unit}]')
ax.set_ylabel(f'Intensity [{intensity.unit}]')
plt.show()
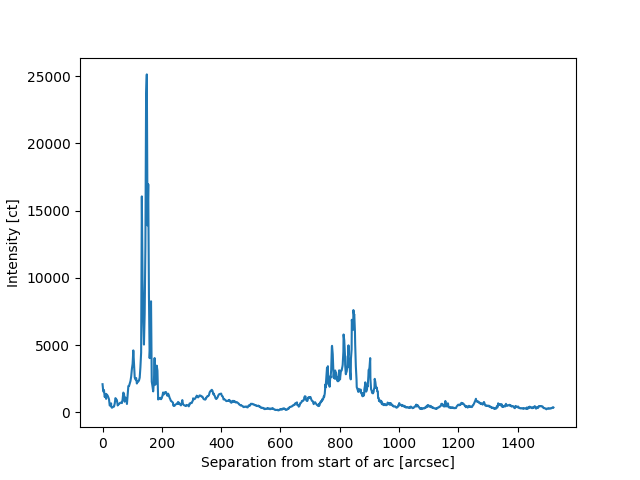
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.849 seconds)